|
Programming an Rpd report.
We must begin knowing that
Rpd files are specially to generate forms such
as invoices, receipts, etc.
We said that Rpd
files were Rpv data files, so we will need to prepare an Rpv file
first to begin.
Example of an
"Rpv" report to generate an "Rpd". (This
example is in the VB sample application).
Suppose that the following
text will be saved as "c:\templates\template_1.rpv".
report_title=Employees
report (format RPD)
Papersize=letter
barwidth=2
$a=400
$b=1400
$c=4500
$1=3200
$2=3300
spacing=250
[header]
{f=arial;s=16}
{pic=rpvlogo.bmp,400,400,1200,800}
{\n;\n;1900;c=2;b=y} Rpv Sample ID. {c=0;b=n;\n;\n;\n}
{LINE=400,10000;\N}
[data]
{s=10;$a;u=y;b=y} @emp_id {$b} @emp_name {u=n;b=n;\n;\n}
{s=8}
{$a} Address: {$b} @emp_address {$c} Phone: @emp_phone
{\n}
{$a} E-mail: {$b} @emp_e_mail {\n}
{$a} Birth date: {$b} @emp_birth_date {\n}
{$a} Area: {$b} @emp_area {$c} Salary: @emp_salary {\n}
{$a} Schedule: {$b} @emp_schedule {$c} Start date:
@emp_start_date {\n;\n;\n}
{LINE=400,10000;\N}
{pic=background.jpg,400,4700,5000,3000}
{w=3;box=400,4700,5000,3000;\n;\n;\n;w=1}
{s=20;u=y;b=y;i=y;c=1;2400} Rpv sample ID {\n;\n;\n}
{s=8;b=n;u=n;i=n;c=0}
{a=c;$b} Photo N/A {\n}
{a=r;$1}ID Number: {$2;a=l;b=y} @emp_id {b=n;\n}
{a=r;$1}Name: {$2;a=l;b=y} @emp_name {b=n;\n}
{a=r;$1}Area: {$2;a=l;b=y} @emp_area {b=n;\n}
{a=r;$1}Schedule: {$2;a=l;b=y} @emp_schedule {b=n;\n}
{a=r;$1}E-mail {$2;a=l;b=y} @emp_e_mail
{b=n;spacing=350;\n}
{s=15;600;bar} @emp_id {nobar}
{pic=@emp_id.bmp,450,4750,1800,1800}
{box=450,4750,1800,1800} |
If you read this file with
Rpv in you should see the following.
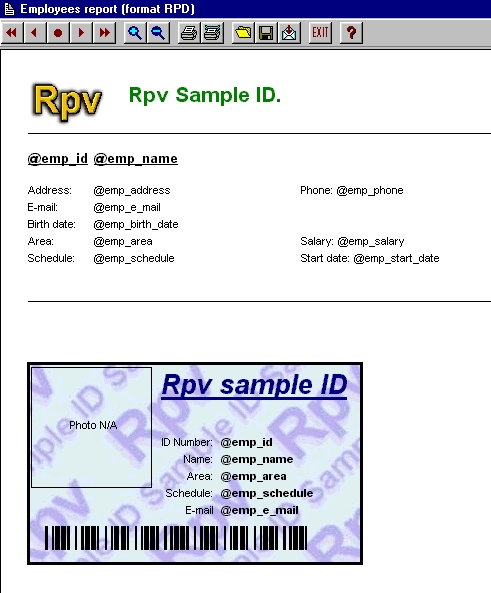
Please observe that
instead of names, e-mails, id numbers you see an "@"
char and the name of a variable.
The variables must begin with the "@" char in all of
cases.
After we have the Rpv
report contaning this, we have to write an Rpd
report with the following format. (This file must be saved with Rpd
extension)
Template=c:\templates\template_1.rpv
@emp_id=11099
@emp_name=Carlos Campos
@emp_address=Independencia 990
@emp_birth_date=05/06/1978
@emp_phone=4766-2425
@emp_e_mail=ccampos@lortotua.com
@emp_area=Aplicaciones
@emp_salary=1.300,00
@emp_start_date=01/03/2001
@emp_schedule=13 to 17:00 |
First line that we see
identifies the template that will
"receive" the rest of the data.
After that, in any order, we must place the variables, equals
sign and a literal value for it.
It is
really important to know that all the variables must be declared
in the Rpd report. This means that if there is
no value for @emp_e_mail, the variable must be present anyway with no value.
If some variable is ommited, then the application will interpret
that is a literal and not a variable.
Example:
@emp_phone=4766-2425
@emp_e_mail=
@emp_area=Aplicaciones |
Observe that @emp_e_mail
variable is declared even when doesn't have any value.
See also:
See Rpv
sample application.
|